Five bar parallel Scara
-
@bondus My ideas for better Z accuracy are (sorted by cost, cheapest and easiest first):
- counterweights at the other side of all hinges at the opposite side of the arms (leverage law or ball bearings could produce your 0.3 mm differences)
- hinges supported with two arms each vertically, so the hinges are more precise
- hinges with metal material
-
@JoergS5, I really think that some critical parts of the arm should be machined. Tiny errors in precision in the parts holding the proximal arms are amplified further out. Possibly you could make some clever parts where you could tune it by tightening/loosening different bolts. This is not unique for this kind of robot arm, any arm moving by rotating a join will have the errors amplified. Linear rails are far easier to use.
My design with the whole arm assembly moving up and down on the z-axis is tricky to design. There is very little room to place screws from the lower part to the upper part, to preload the bearings. The large pulleys and the goal to keep the arms rotation range as big as possible does not make it easy. The current version is far from ideal.
I am working on a better version, but every time I start fusion I lose a day. It's very mesmerizing to 3D CAD.
I installed an old precision piezo to measure the Z error properly. I had one of the the old crummy versions with a drilled piezo element laying around. It still works fine.
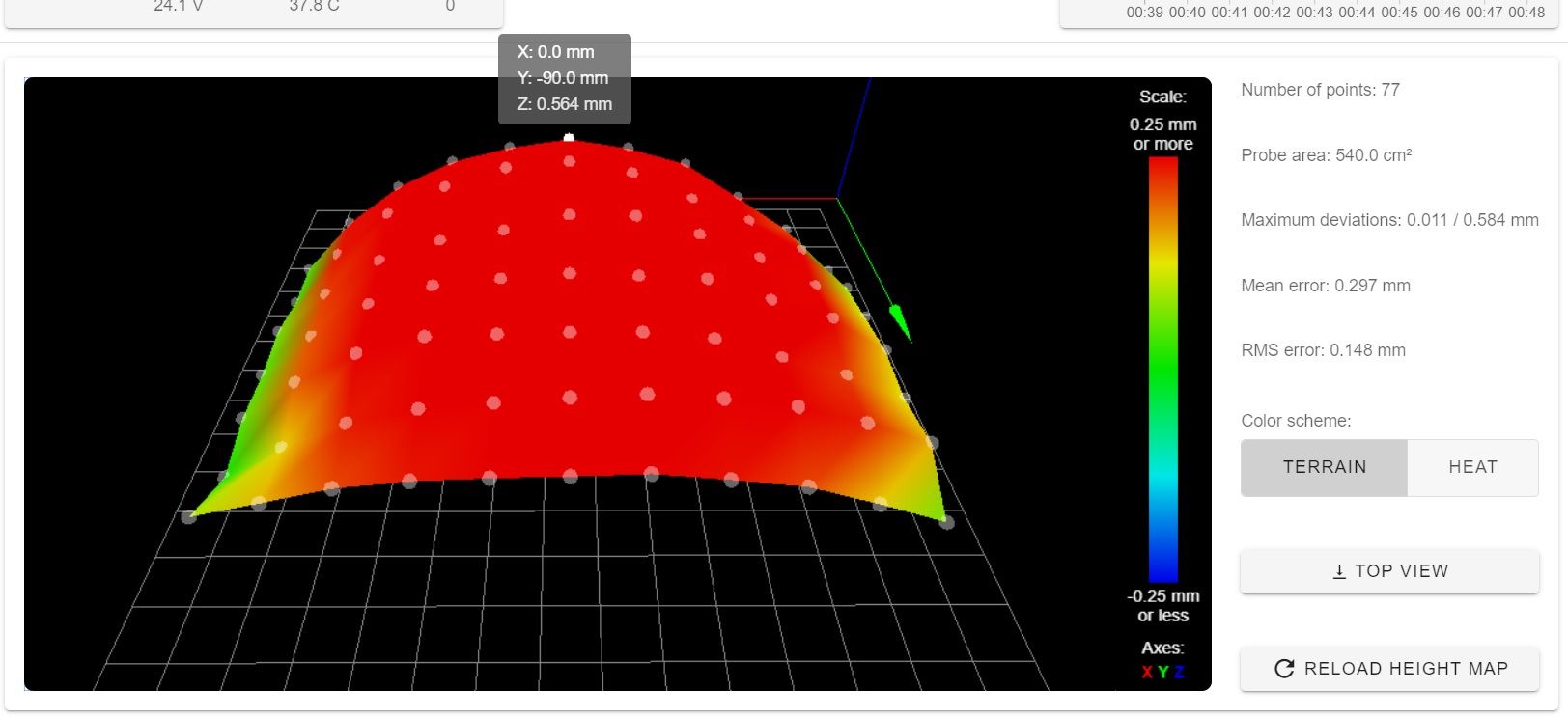
I can see that the arms lifts the actuator the further out the actuator is. It's not due the tower being at the wrong angle, or the weight of the arms bending it down. Some other angle(s) are wrong. It's a complicated machine

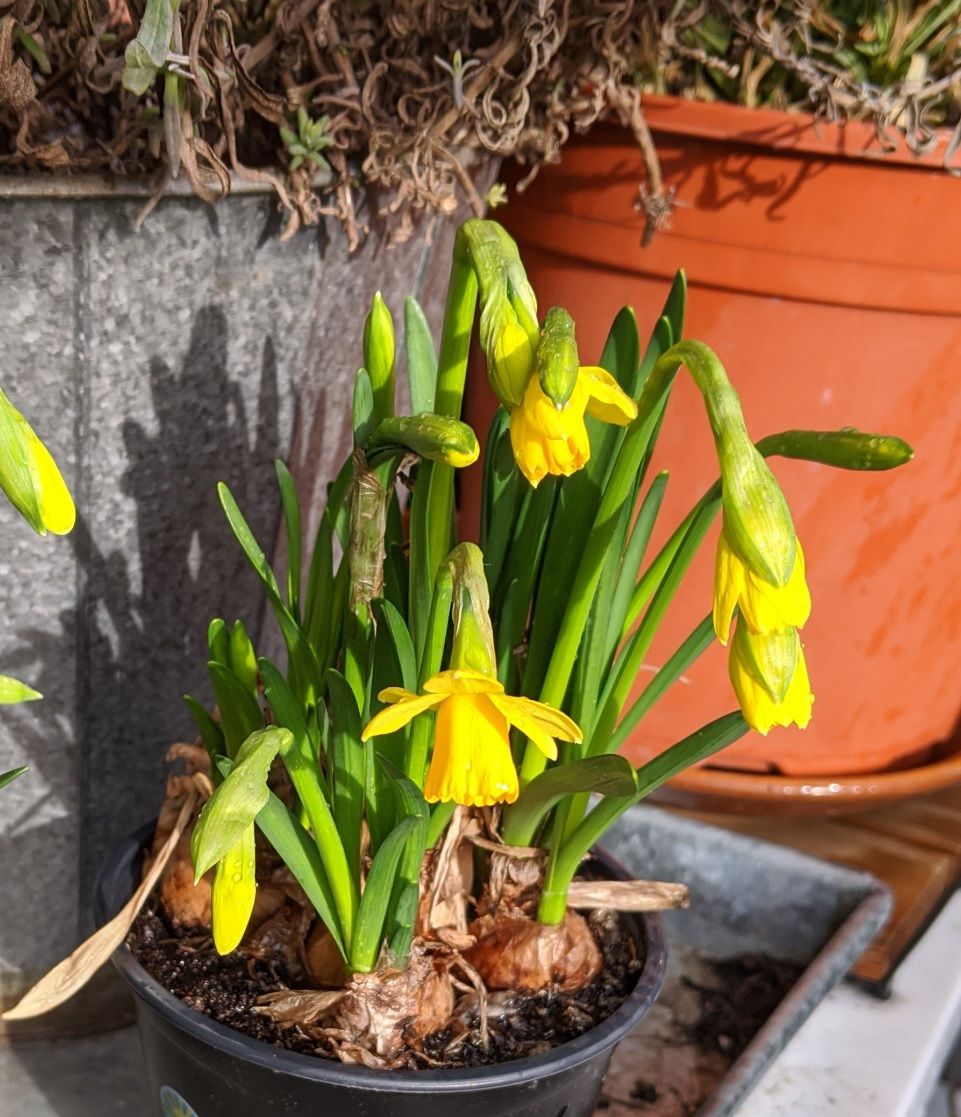
It's officially spring here now, at least on my balcony. The bulbs from last year are flowering.


-
@bondus Holy crap, is that a flower? It's the dead of winter here. I feel like I haven't seen colours like that in ages.
-
@bondus Nice narcissus, it becomes spring!
I was thinking a lot about precision of parallel scara the last months, especially of the hinges. Additional ideas to my last ideas are:
- supporting the arms by steel wires like at some cranes like in
 This goes into the direction of tensegrity also.
This goes into the direction of tensegrity also. - from compliant mechanism replacing ball bearings with something like in https://3dprint.com/252086/developing-3d-printed-soft-actuators-for-robotic-arms/ (I mean the black one, called revolute joint in the image) or https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=0MQXoVKrRbo One can get about 30 degree with the first one, called butterfly hinge also. Other ideas are Hylite hinge and crossed springs (german: Kreuzfedergelenk), but one gets only about 15 to 30 degree rotation. Hylite is very interesting, because the multimaterial polypropylene with something carbon based could be printed easily with the new multimaterial printers.
- trying calibrate the actuators separately by rotating them the three directions each, so hinge errors are minimized. But I didn't calculate how to do it best.
I final idea: we had some interesting discussion about uneven printing, so a fast z movement would be interesting. This movement can be small (layer height * small number), so some piezo actuator which moves the hotend could be used. This piezo mover could correct your arm height errors also. The supplier https://www.cedrat-technologies.com/en/technologies/actuators/piezo-actuators-and-electronics.html show what is possible with stacked piezo elements.
- supporting the arms by steel wires like at some cranes like in
-
It's fun to see Fusion 360 struggle with the five bar kinematics. It's doing a surprisingly good job.
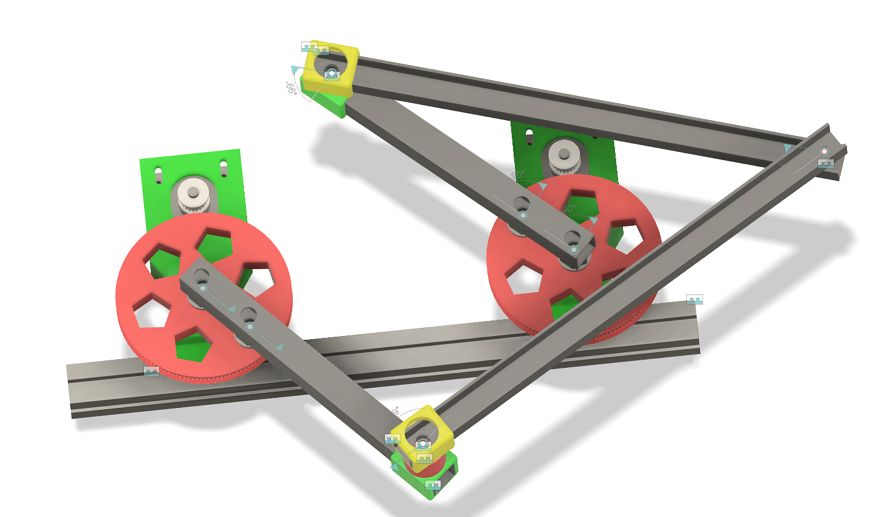
I'm working on a smaller version with greater movement range that will eventually evolve into a version 2 of the printer. The current version has many flaws.
I wish I had a lathe and a router to make some small items. There are some critical parts in the joints that would benefit greatly from being made in steel or aluminium. Perhaps there is a makerspace nearby...
-
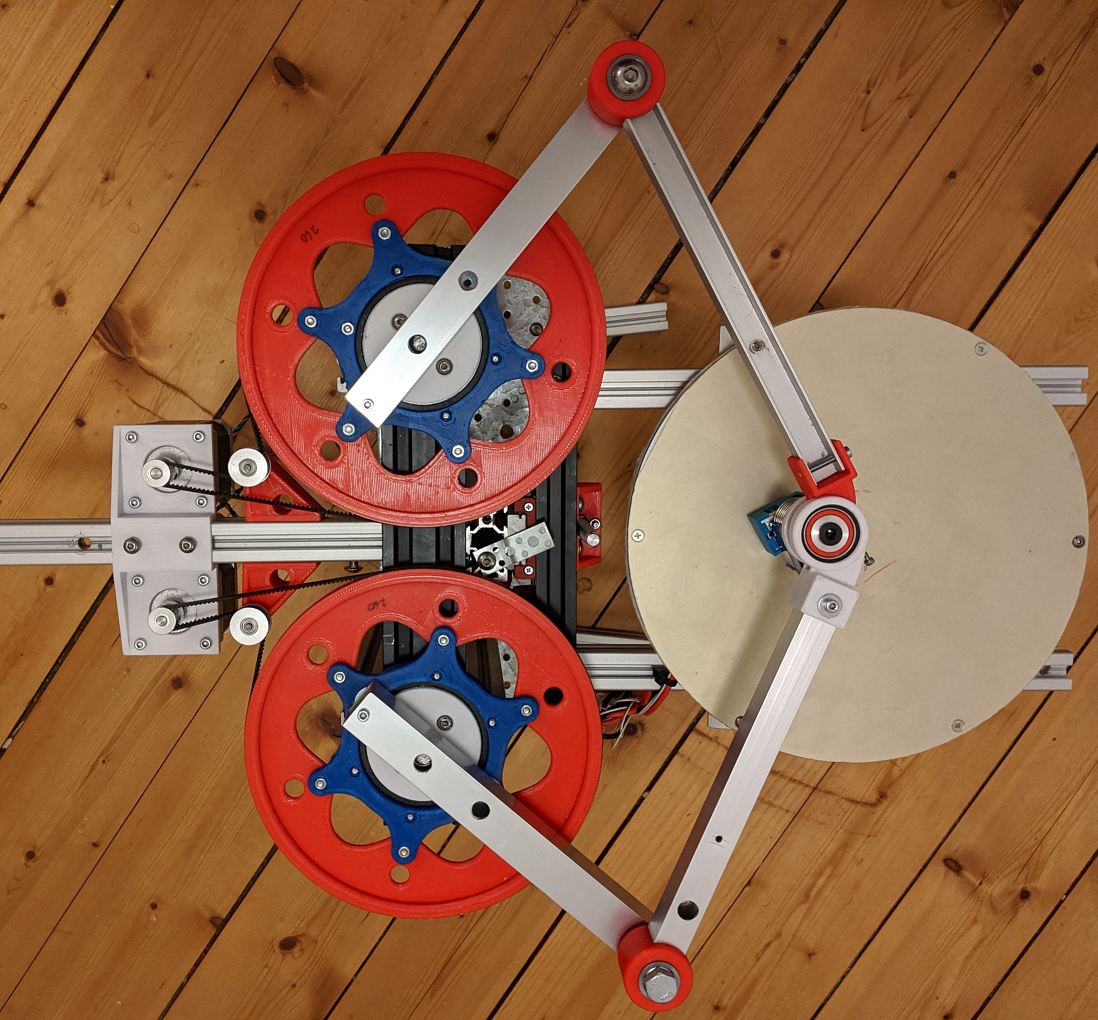
@bondus this is the direction I go also. My construction has a larger big wheel (your red ones), so the gear between stepper and wheel is about 1:30 (results stepper 10 turns/s => arm hotend speed about 10/30*300 = 100 mm/s). The hinges are critical imho, so I support the axis with two ball bearings each. I have not decided yet wheter I will use two arms each or using wires to stabilize. Instead of steel arms you could use carbon fiber also: similar e-module, lighter and less thermal expansion, but more expensive and more difficult to glue/connect.
-
@JoergS5 This version has two ball bearings too, behind the pulley. I preload the poor deep groove bearings by tightening a lock nut a little bit. They are really not made for that kind of axial load, but it works. I have some angular bearings that I might use further on, but I save them for now. They are prone to fall apart and were pretty expensive.
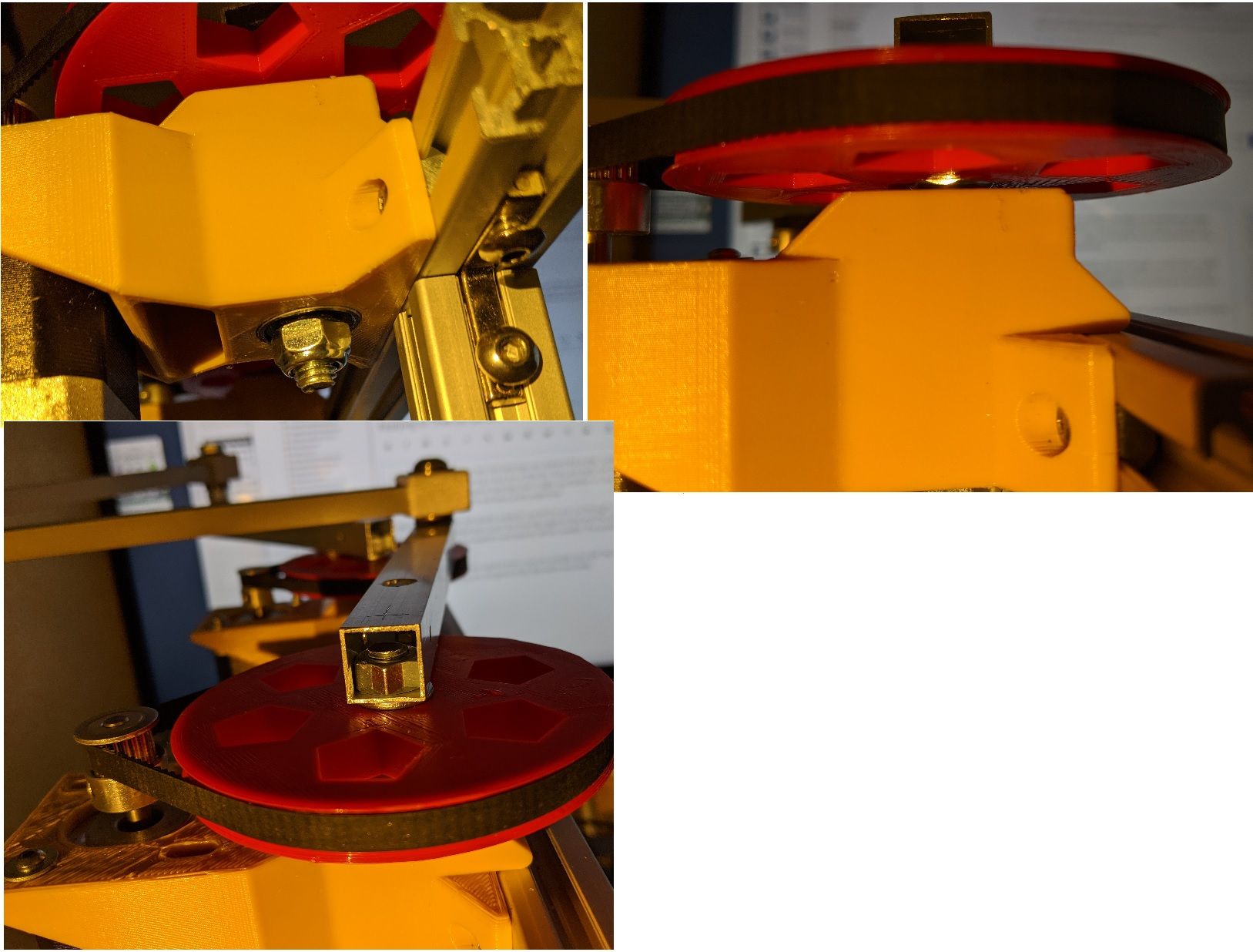
A very simple construction. Two plastic parts, two bearings and three nuts.One idea to avoid the soft plastic could be use let the axle run through a drilled hole in a 3060 extrusion or other metal part, push the bearings against that and then push the arm directly onto the bearings. Some washers and spacers will be needed. The printed plastic parts would just hold things in place.
The thin walled aluminium square arms I use are actually very stiff. The U-beams in the drawing are just for testing, they are not good at all, they twist very easily.
-
Only 0.15mm deflection when adding 180g to the actuator. (That big bearing weighs 180g). Not bad.
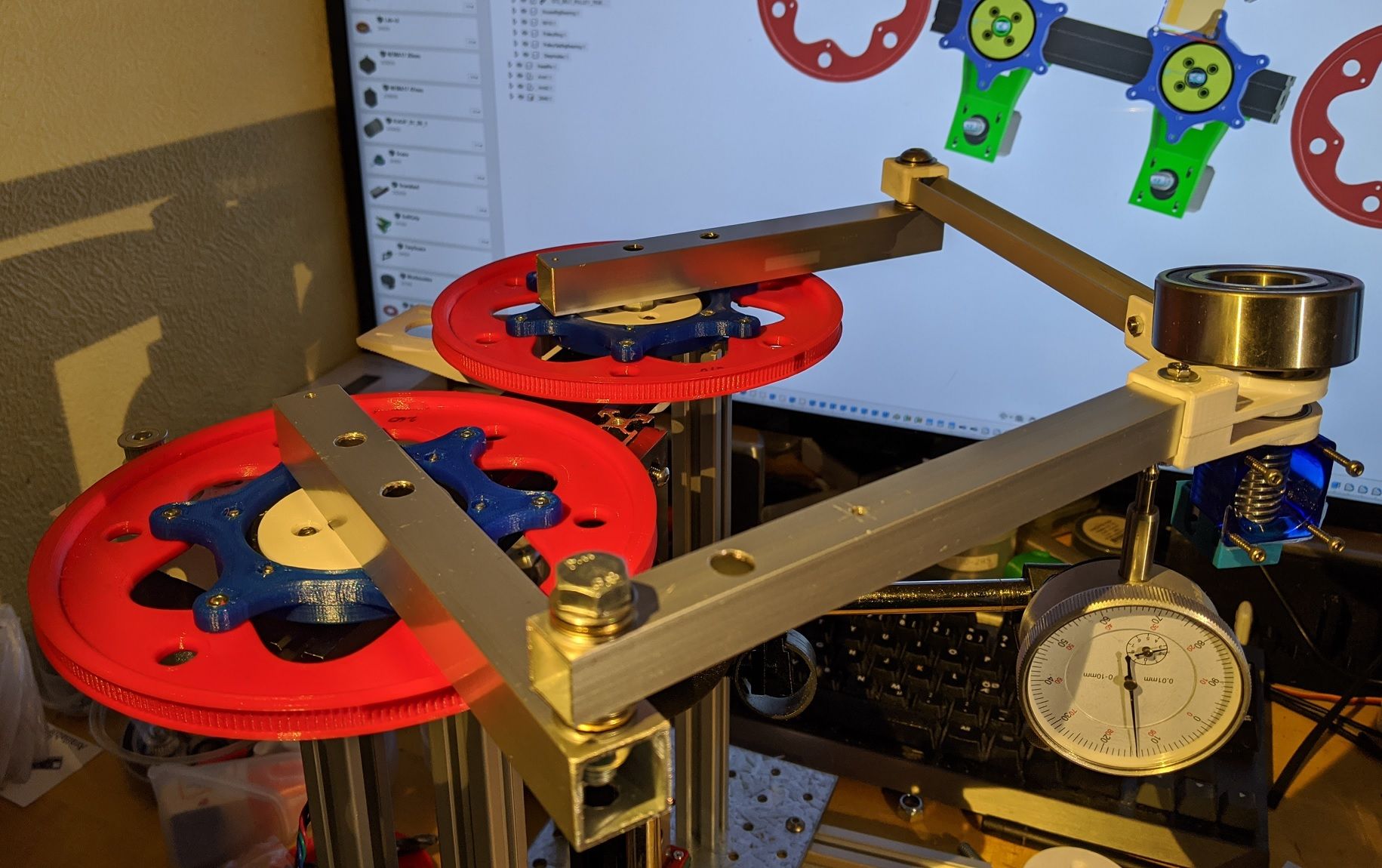

I went for a bigger bearing at the shoulder, a 6810 at the top and a small ID 8mm below the 2040 extrusion. It made a massive difference with a big diameter bearing.
The weak point now is definitely the elbows.
-
@bondus I like how you constructed the "big wheels", which makes 3D printing easier, printing multiple parts. May I copy this idea?

-
@JoergS5 I split them because it takes very long to print the pulleys, they have to be printed fairly slow to get decent teeth. And it makes easier to swap pulley size or quickly modify the inner part. Copy all you want, perhaps you can design better looking spokes.
-
Just missing two endstops and an extruder and it's ready to go.
I spent hours calibrating it yesterday. Since nothing is really adjustable that meant filing on plastic pieces and very slightly bending and twisting the arms.
It is critical that all joint bearings work in the same plane, it is an overconstrained system in the z-plane. If not all 5 joints are in the same plane they will fight each other and create a strange z-deviation map.
Any errors can easily be seen by keeping the actuator at the same spot but changing the arms to different work modes.I'll put adjustable endstops at right angles, 0deg for right arm and 180deg for left arm. That way they are easy to calibrate.
Possibly they are better placed straight back if I will use work mode 1 or 4. It can be a bit tricky to home the machine from an unknown position. -
After some quick tuning of the hotend and more mechanical calibrations I managed to print this stunning benchy, at 120mm/s and 2500mm/s^2 acceleration. I'm surprised!

-
Some videos of the beast in action:
Printing of a calibration item at 120mm/s.
https://youtu.be/yubS3_OUhQsSame thing but in a different work mode (arms at a different angle). I have tried to make this machine as flexible as possible to be able to test all cases of the firmware. If I extend the outer arms a little bit the inner arm can travel all the way around to the backside. Right now the hotend collides with the pulleys.
https://youtu.be/1IpzSe83RkQ -
@bondus Thanks for sharing the videos. Good idea to make the proximal inner arms shorten than the actuator difference. My arms are longer and I have some problems (I support the axes at the top with a bridge and the arms are in the way).
What do you mean by "hotend collides with the pulleys". At which time?
-
@JoergS5 The short proxial arms have the drawback that it gets quite a small reach. It could be made better by putting one of the proxial arms a bit higher up to not collide with the other one, and make it longer. It would work good for work mode 1 or 4 depending on which arm is longer.
It's hard to pick arm lenghts that are good for everything. And it's hard to avoid colliding with something, other arms, the frame, motors ...The hotend collides with the pully if the proximal arm points straight back and the distal arm points forwards, or if both proximal arms points too far to the sides. It has a tendecy to do that when I home it. Homing only works reliably if it starts with the proximal arms pointing forwards. I need a low resolution absolute encoder to be able move the arms in a safe way to the homing endstops.
The distal arm just needs to be around 20-25 mm longer to make many more moves possible.
It is possible to move the hotend to the backside if you navigate it on the side around the pulleys. I should handcraft some gcode to show off what kind of moves it is capable of, it is very flexible.
-
@bondus Thanks for explaining. I once had the idea to design variable arm lengths and actuatuar difference and decide from the object-to-print which configuration to use: print area ok, configuration so that the goal is reached to have maximum precision or speed. Maybe I come back to this idea (telescopic arms?).
-
@bondus If you want to improve your hinges between proximal and distal arms, you can consider using bigger support surfaces. I think this is the reason why the commercial robots have such big diameters of their hinges (or Mitsubishi RP series). For low friction between surfaces/washers, PTFE on PTFE has low friction.
-
I have had some more adventures in calibration, the grid test model is almost 100% correct now.
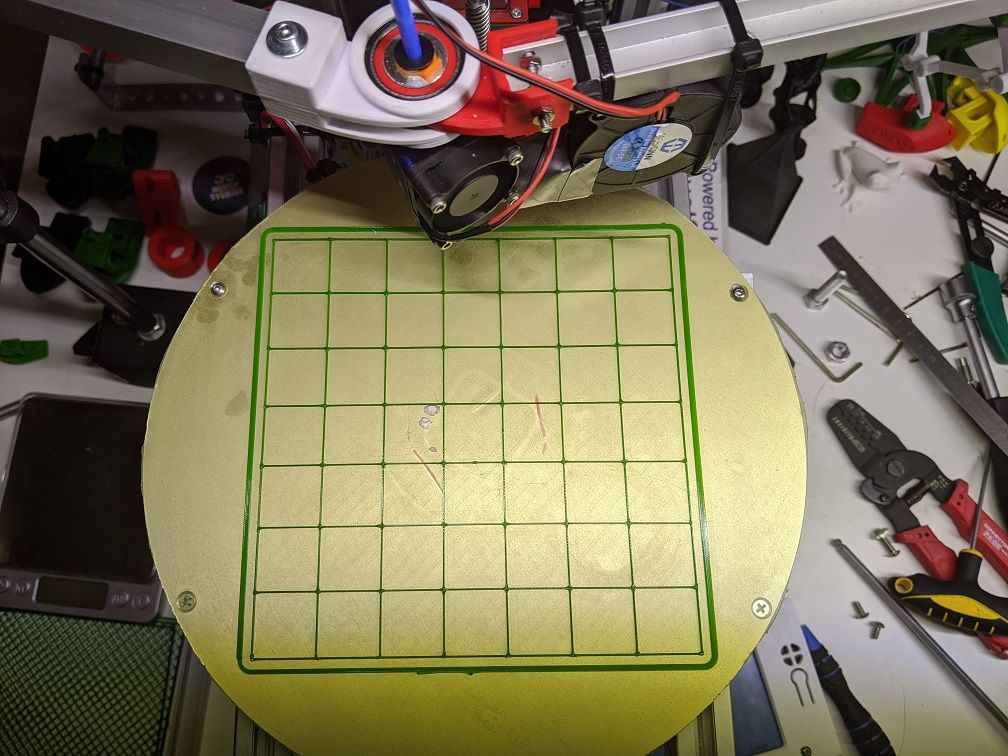
One of the trickiest parts to calibrate on a rotating machines are the angles. I had that in mind when designing this machine and made sure that it would be reasonably easy to measure critical angles. The key trick is that the homing positions are at 0 and 180 degrees, and that the inner arms can be lined up. Simply using a straight ruler and a few GCODE macros the errors can be measured and homing positions and steps/deg can be adjusted. It is very important that the angles are correct within about 1%% or there will be large errors in the cartesian space at some positions.
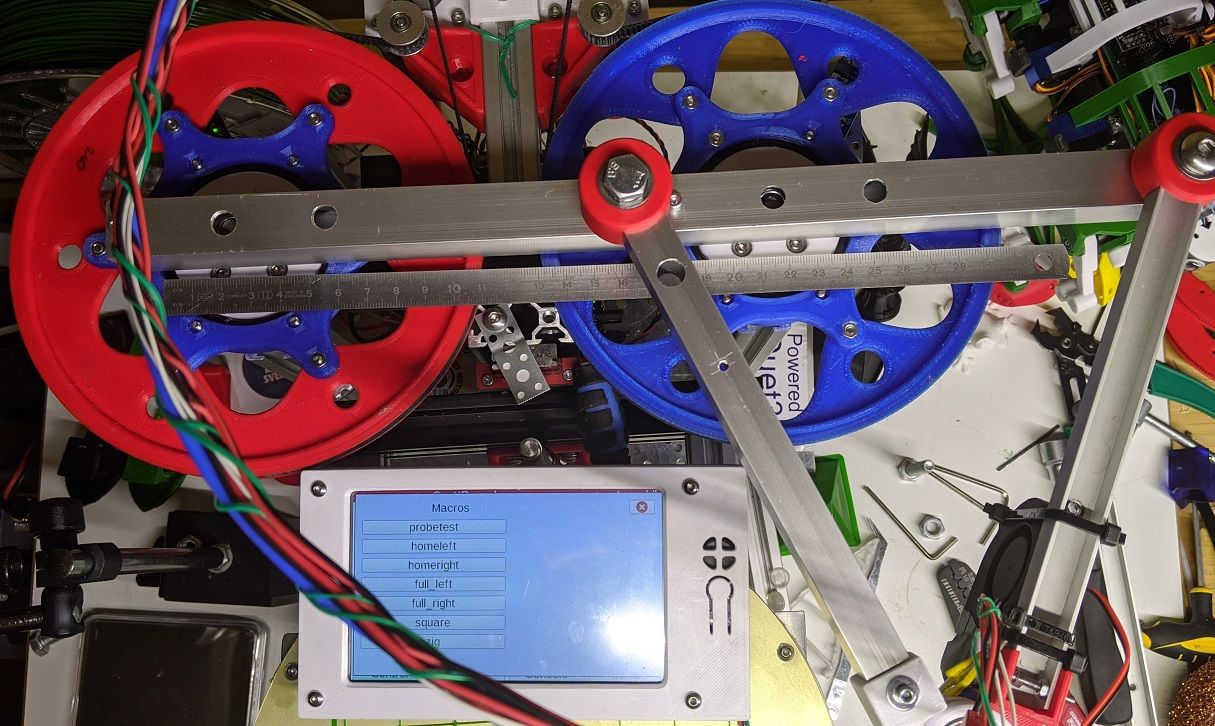

The trusty old dial gauge has had it's uses too making sure the pulley are centered and round:
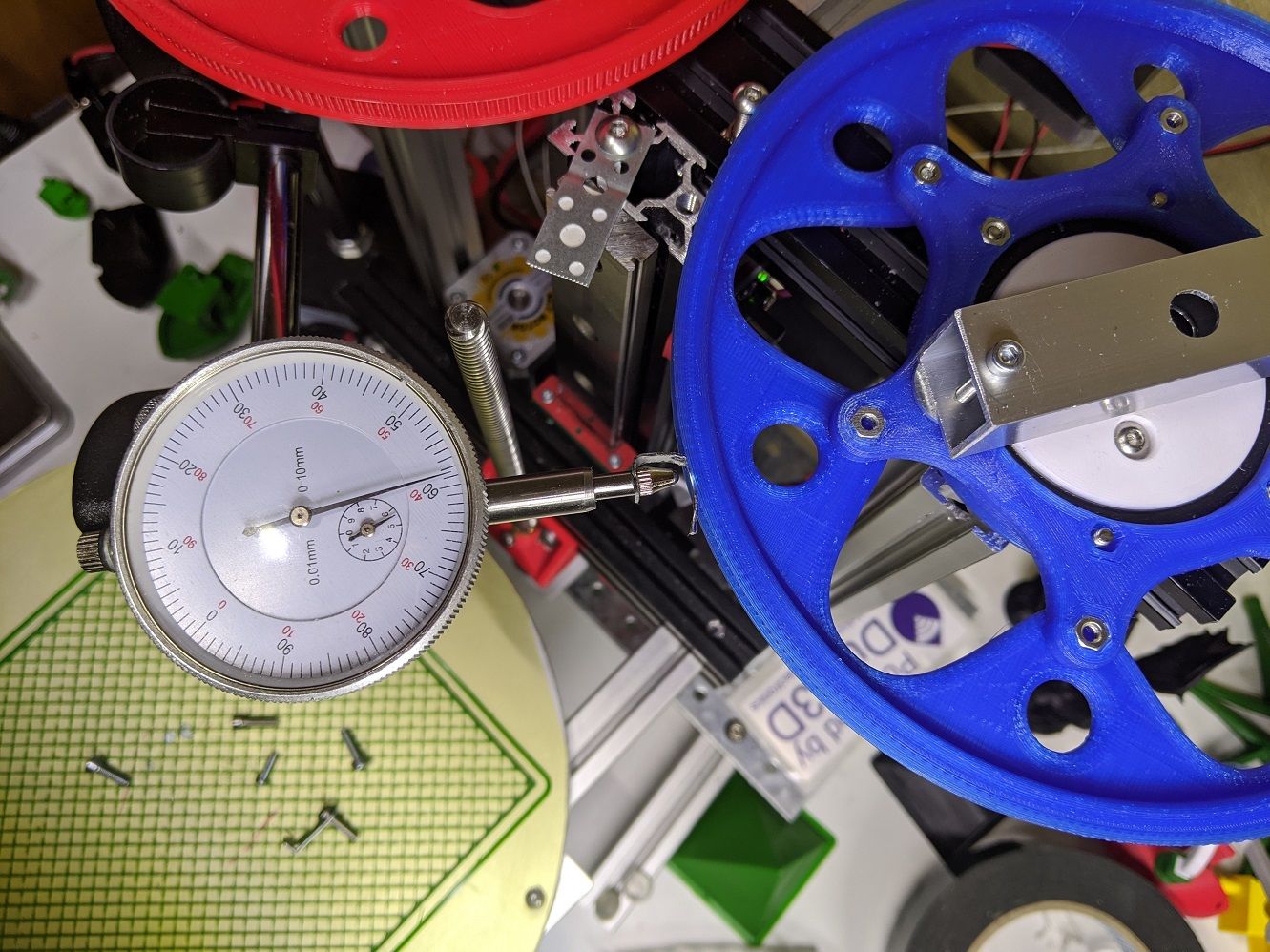
The real world steps/deg was off by over 1% from the calculated ideal. I'm not sure if it is my printed pulleys or the generic 16t chinesium pulleys on the motors that are to blame.
It took a few tries to get the printed pulleys working right, shaving off 0.1mm on the tooth surfaces made it properly sized. Fortunately the belt will not teeth properly if it is too big or too small, instant verification of tolerances.
I should create a test model that can be printed, measured and fed into a program to do the calibration instead. The math for this is non-trivial though, there are lots parameters to tune. Some kind of numerical solving algorithm would probably be needed. It would be a lot more user friendly though.
-
@bondus you're a little ahead of me, but I'm catching up!

I want to measure angles by an optical encoder attached to the big wheels, which has higher precision than to measure at the steppers imho. But I start with a normal endstop also, attached to the big wheel.
To avoid backlash at the pulleys or hinges, I want to try a spring that pulls the axle to one side.
-
@JoergS5 said in Five bar parallel Scara:
If you want to improve your hinges between proximal and distal arms, you can consider using bigger support surfaces.
The current solution in the "elbows" with a heavily preloaded thrust bearing to do most of the work works very well. The thrust bearing actually does the radial load as well as the axial load, and it's the friction between the bearing house and the arms that holds everything in place! The printed parts is holding the thrust bearing in place, but plastic is soft.
A mechanical engineer would definitely not approve of this solution. But it works and it's a very simple and compact solution.And bigger is better for sure. I used 8x16 bearings before, now they are 10x18.